Important issues covered in the Science Syllabus
Over the past year there had been a lot of topics that had been taught to us.
You can check HERE to see a broad scheme or schedule of our teachings. Here I will talk about several important issues that were taught to us in Secondary One.
The first sections is about what is Science and why Science is important.
The notes explain that Science stands for scientia in latin, which means "knowledge".
It also explains to us the three major elements involved in the study of Science, namely: Attitudes, Processes and Methods, Products. Afterwards it also introduced to us the benefits of Science and what would happen if Science were abused.
This section of this topic was all in theories but they are very important to us as all the things it talked about were like ground rules and foundations for the studying of Science.
The second section is about the Science labs. They include the rules and regulations in the lab and some common apparatus used. The notes focused on the Bunsen Burner and it is crucial to know how it works as many experiments requires heating and we need to know how to use the Bunsen Burner safely so that there are no risks of a strike-back, a gas leak or anything dangerous.
Here's a very interesting song about the Bunsen Burner, it is a very good way to learn about the various controls and properties of a Bunsen Burner.
Under this topic we learn about the use of all kinds of measuring equipment, from the simple meter rule that measures length to the accurate burette that measures the volume of liquids.
I will focus on one specific measuring equipment here, called the vernier calipers, which I found very difficult to understand at first.
Zero error often occurs when the vernier calipers are used. The zero error occurs when the zero marks and the main scale failed to align when the jaws are completely closed. There are 2 types of zero errors: Positive zero error and the negative error. The positive zero error is when the initial reading overestimated as the zero mark of the vernier scale lies on the right of the main scale. The negative zero error is when the initial reading is underestimated as the zero mark of vernier scale lies on the left of the main scale.Lastly, we are taught how to use the micrometer screw gauge. The micrometer has 2 scales: the main scale on the sleeve, and the circular scale on the thimble.
Method of reading:
1) Read the main scale reading at the edge of the thimble
2) Take the thimble reading opposite the datum line of the main scale
3) The reading is found by adding the main scale reading to the thimble reading
This section of Science was a very practical and mathematical area of it. It requires basic mathematical skills and a strong understanding of concept.
Brownian Motion is the presumably random moving of particles suspended in a fluid resulting from their bombardment by the fast-moving atoms or molecules in the liquid.
A simulation of Brownian motion below:

Diffusion, on the other hand, is a very basic principle of liquids and gasses. When diffusion occurs, molecules in an area of relatively high concentration move to an area of relatively low concentration.
In this topic we were also taught the three states of matter: Solids. liquids, and gases. Differences between the three were introduced to us as well.
Topic 1: Science as an Inquiry
This topic is separated into two sections, and both of them are extremely important and useful throughout the entire year.The first sections is about what is Science and why Science is important.
The notes explain that Science stands for scientia in latin, which means "knowledge".
It also explains to us the three major elements involved in the study of Science, namely: Attitudes, Processes and Methods, Products. Afterwards it also introduced to us the benefits of Science and what would happen if Science were abused.
This section of this topic was all in theories but they are very important to us as all the things it talked about were like ground rules and foundations for the studying of Science.
The second section is about the Science labs. They include the rules and regulations in the lab and some common apparatus used. The notes focused on the Bunsen Burner and it is crucial to know how it works as many experiments requires heating and we need to know how to use the Bunsen Burner safely so that there are no risks of a strike-back, a gas leak or anything dangerous.
Here's a very interesting song about the Bunsen Burner, it is a very good way to learn about the various controls and properties of a Bunsen Burner.
Topic 2: Measurements
Under this topic we learn about the use of all kinds of measuring equipment, from the simple meter rule that measures length to the accurate burette that measures the volume of liquids.
I will focus on one specific measuring equipment here, called the vernier calipers, which I found very difficult to understand at first.
A vernier caliper can be used to measure the both the external and internal dimensions of something. That function is often used when measuring the thickness of a cup (external diameter-internal diameter/2=thickness of the cup).
The steps to using a vernier calipers are:
1. Close the jaws (see above picture) to ensure the 0 mark are straightened on the vernier scale and the main scale. This is to check for zero errors, which will affect the final reading.
2. Adjust the jaws to clamp onto the object.
3. Check the reading on the main scale, the reading should be a x.x number, where the 0 on the vernier scale is the stopping mark.
4. Check for the lined up mark between the main scale and the vernier scale, the number on the vernier scale is recorded. The unit is 0.01 cm.
5. Add the reading on the main scale with the reading on the vernier scale, the total is the length of the object.
Method of reading:
1) Read the main scale reading at the edge of the thimble
2) Take the thimble reading opposite the datum line of the main scale
3) The reading is found by adding the main scale reading to the thimble reading
This section of Science was a very practical and mathematical area of it. It requires basic mathematical skills and a strong understanding of concept.
Apart from measurements, the notes also provided explanations on how to use various other instruments. At the end, we learnt about the SI units of all the measurements, and here they are:
Topic 3: Classification of Matter
In this topic the Kinetic Particle theory was taught to us. Kinetic particle theory states that the matter is made of tiny discrete particles, which are in constant and random motion. This statement is supported by two other subjects that we learnt named the Brownian Motion and Diffusion.Brownian Motion is the presumably random moving of particles suspended in a fluid resulting from their bombardment by the fast-moving atoms or molecules in the liquid.
A simulation of Brownian motion below:

Diffusion, on the other hand, is a very basic principle of liquids and gasses. When diffusion occurs, molecules in an area of relatively high concentration move to an area of relatively low concentration.
In this topic we were also taught the three states of matter: Solids. liquids, and gases. Differences between the three were introduced to us as well.
I find this section of the topic quite simple and useful at the same time. It was fairly easy to understand.
Topic 4: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
In this topic we learnt about the differences between compounds and mixtures:
We also had to memorize some things from the periodic table:
As well as certain chemical formulas such as Na+Cl2=NaCl
We conducted several experiments such as testing out the properties of some elements and see what would happen if you A)combine them physically (mixture) B) combine them chemically (compound). It turned out that a mixture would have both elements' properties while a compound could share similar properties with only one or even none elements.
Topic 5: Separation Techniques
This topic is very complex, and I will introduce some important and complex separation techniques.
Distillation:
Distillation is the technique used to separate two miscible substances, such as common salt and water. The theory uses the different boiling points of different substances. The process is as follow:
The solution is first heated, the substance with the lower boiling point will evaporate first and float upwards. It then does to the condenser where it is in gas form. Slowly it condenses and rolls into a receiving flask. The other substance with a higher melting point is then left behind.
Crystallization:
Crystallization is a process of forming crystals. It is also a method for separating dissolved solids from a solution. It is quite similar to evaporation, and is often confused with it.
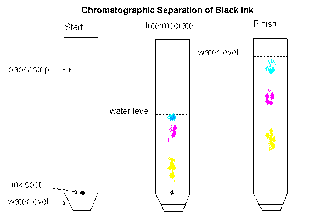
Chromatography:
"In paper chromatography, there are two factors which the movement of each substance in the mixture need to depends on.
The substances separated by chromatography do not have to be colored. Colorless substance can be made to show up by spraying the paper with a locating agent. Then reacts with each of the colorless substances in order to produce a colored product.
We often used chromatography to identify the substances in a mixture. It is commonly used in hospital. It help doctors to find out whether the patient has diabetes, if paper chromatography might fund out whether sugar is present in the patient's urine.
Chromatography can also used to identify different dyes used in food."
(http://library.thinkquest.org/11430/research/chromato.htm)
- The solubility of the substance in the solvent. The substance moves with the solvent easily if the substance is very soluble in the solvent.
- The adsorption of the substance on the filter paper. Some solids are able to attract other substance strongly and hold them on their surface. This is called ADSORPTION. The substance will not move with the solvent easily if the substance in the mixture is absorbed strongly by the filter paper.
The substances separated by chromatography do not have to be colored. Colorless substance can be made to show up by spraying the paper with a locating agent. Then reacts with each of the colorless substances in order to produce a colored product.
We often used chromatography to identify the substances in a mixture. It is commonly used in hospital. It help doctors to find out whether the patient has diabetes, if paper chromatography might fund out whether sugar is present in the patient's urine.
Chromatography can also used to identify different dyes used in food."
(http://library.thinkquest.org/11430/research/chromato.htm)
Topic 6: Cells
In this topic we learnt about the characteristics of a cell, and the differences between an animal cell and a plant cell.
Firstly, what is a cell?
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.Here is a typically animal cell:
There are many differences between an animal cell and a plant cell:
Conclusion: That is my coverage on the important issues covered in the Science Syllabus. Over the past year a lot of things had been taught to us, and it is hard to say which one is the most important. In the end, we all need to study them with equal concentration and focus so that we could do well in tests.










没有评论:
发表评论